Check your CPU’s clock speed in Task Manager, CPU-Z, or BIOS and compare it to the manufacturer’s default. Revert to default settings via BIOS or tools like Intel XTU if overclocked.
If you’ve ever wondered whether your CPU is overclocked, you’re not alone. Overclocking, which involves running your processor at a faster speed than its base clock, is common among enthusiasts looking to boost performance. However, overclocking can also cause your system to run hotter, use more power, and even shorten the lifespan of your CPU.
What is Overclocking?
Before we dive into the steps, let’s quickly define overclocking. Overclocking is the process of manually increasing the clock speed of your CPU beyond the factory-set specifications.
Manufacturers set default speeds for a reason, so overclocking can lead to increased heat generation and potential instability. However, if done correctly, it can provide a performance boost, especially in tasks that demand high processing power, like gaming, video editing, or 3D rendering.
Why Does Overclocking Matter?
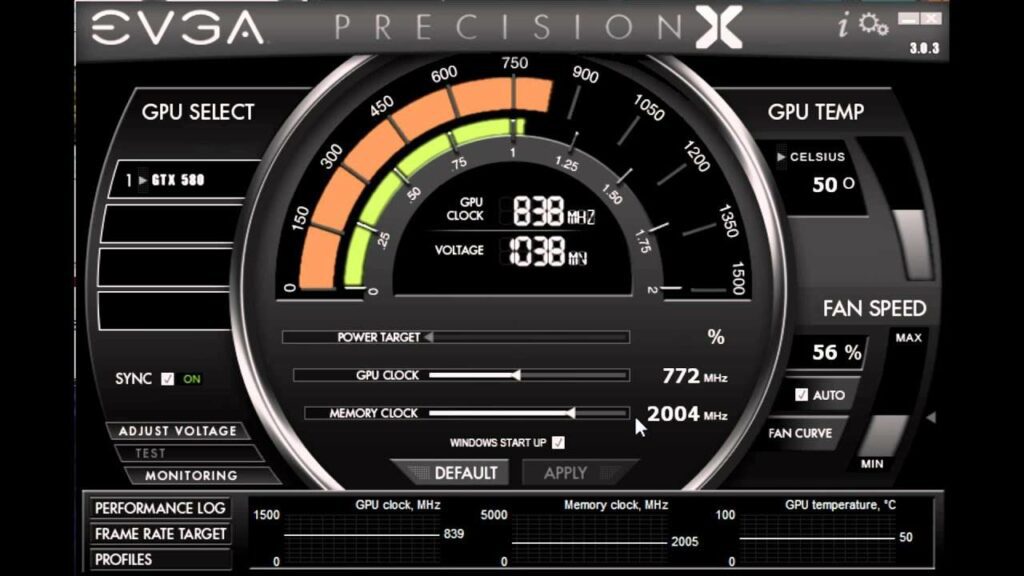
While overclocking can boost your system’s performance, it comes with some risks. These include:
- Increased heat: Overclocking generates more heat, requiring better cooling solutions.
- Higher power consumption: Overclocking increases the electrical demands of your CPU.
- System instability: Pushing a CPU too far can lead to crashes, errors, or instability.
- Potential damage: Prolonged overclocking without proper cooling can cause long-term damage to the CPU or other system components.
What to Do if Your CPU is Overclocked?
If you discover that your CPU is overclocked and you’re unsure whether you want to keep it that way, here are some options:
- Leave it overclocked: If you’re happy with the performance boost and have good cooling, you can continue to use it overclocked.
- Restore default settings: If you want to revert to the default clock speeds, you can reset your BIOS settings to default or use software tools like Intel’s XTU (Extreme Tuning Utility) or AMD Ryzen Master to dial it back.
How Do I Know If My CPU Is Clocked?
To determine if your CPU is overclocked, you can check its clock speed using various methods. The easiest way is through system monitoring tools, which give you real-time data on your CPU’s performance. By comparing the clock speed to your CPU’s default specification, you can quickly identify if it’s running faster than intended.
Read More: What Games Are Cpu Intensive – A Complete Guide Of 2024!
How to Check Your CPU Speed in Task Manager?
In Windows, you can use Task Manager to check your CPU’s clock speed. Open Task Manager (Ctrl + Shift + Esc), go to the Performance tab, and select CPU. The clock speed will be displayed here. If it’s higher than the stock speed specified for your CPU, it may be overclocked.
How to Check CPU Speed in BIOS?
Another way to check your CPU’s clock speed is by accessing the BIOS settings during startup. Restart your PC, press the BIOS access key (usually F2 or Del), and look for the CPU settings. There, you can view the current clock speed and compare it to the stock frequency listed by the CPU manufacturer.
What to Compare It With?
To confirm if your CPU is overclocked, compare its current clock speed with the stock speed provided by the manufacturer. You can easily find this information on the official Intel or AMD websites. If your CPU speed exceeds the listed base or turbo speeds, it indicates that your CPU is overclocked.
How to Stop a CPU from Overclocking?
To stop overclocking, go into your BIOS or UEFI settings during startup. Reset the CPU settings to their default values or set the clock speed back to the original level. You can also use software like Intel XTU or AMD Ryzen Master to adjust the settings from within your operating system. After making changes, make sure to save and exit the BIOS. If you’re using software, apply the settings and restart your system to ensure the changes take effect.
How to stop a CPU from overclocking?
To stop your CPU from overclocking, go into your computer’s BIOS or UEFI settings. Look for the CPU settings and reset them to the default values. This will return the clock speed to its original level.
If you use software like Intel XTU or AMD Ryzen Master, you can adjust the clock speed from within Windows. Once you’ve made the changes, save and restart your computer to apply them. Make sure to monitor your CPU’s performance after resetting, to ensure it runs at the correct speed. This will also help prevent overheating and system instability.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. How can I check if my CPU is overclocked?
You can check if your CPU is overclocked by using system monitoring tools like CPU-Z, Task Manager, or by checking the BIOS settings. These tools show your CPU’s current clock speed, and you can compare it to the default speed listed by the manufacturer. If the clock speed is higher, your CPU is likely overclocked.
2. What is the default clock speed of my CPU?
The default clock speed of your CPU can be found on the manufacturer’s website, such as Intel or AMD. You can also check the model number of your processor (e.g., Intel Core i7-9700K) and look up its base clock and turbo boost speeds. This will help you identify if your CPU is running faster than the default speeds.
3. Is overclocking my CPU dangerous?
Overclocking can increase performance, but it also increases heat and power consumption. If not properly managed, it can lead to system instability, crashes, or long-term damage to your CPU or other components. It’s important to monitor temperatures and ensure proper cooling if you overclock.
4. Can I stop my CPU from overclocking?
Yes, you can stop your CPU from overclocking by resetting the clock speed settings in the BIOS or using software like Intel XTU or AMD Ryzen Master. Simply return the CPU settings to their default values, and your CPU will run at the manufacturer’s stock speed.
5. How do I monitor my CPU temperature after overclocking?
To monitor your CPU temperature, you can use software like HWMonitor, Core Temp, or CPU-Z. These tools show real-time temperature readings, allowing you to monitor how hot your CPU gets while overclocking. Ideally, temperatures should stay below 80-85°C to avoid overheating.
Conclusion:
Checking if your CPU is overclocked is simple with tools like CPU-Z, Task Manager, or by accessing BIOS. Overclocking can boost performance, but it also comes with risks like increased heat and power usage. If you find your CPU is overclocked and you’re concerned, you can easily revert to the default settings in BIOS or using software like Intel XTU or AMD Ryzen Master.

