During video editing I recognized how fundamental the CPU functions because it slowed down my old PC. The performance upgrade from a slower to a faster CPU completely changed the way I work because everything now finishes quickly and smoothly. Every operation on your device depends completely on this component which functions as the fundamental driver of your device performance.
Inside computers the CPU functions as the fundamental component because it performs most automated processing activities. The CPU runs programmed instructions which determines its role in application and task execution. The CPU stands as the “brain” of computer operation while directly determining system performance.
Our upcoming piece explores the insides of your computer CPU for an in-depth study. This article will examine the CPU’s positions in a computer system plus understanding both its critical relevance and its role in running your device activities. You won’t want to miss this!
What Does CPU Stand For?
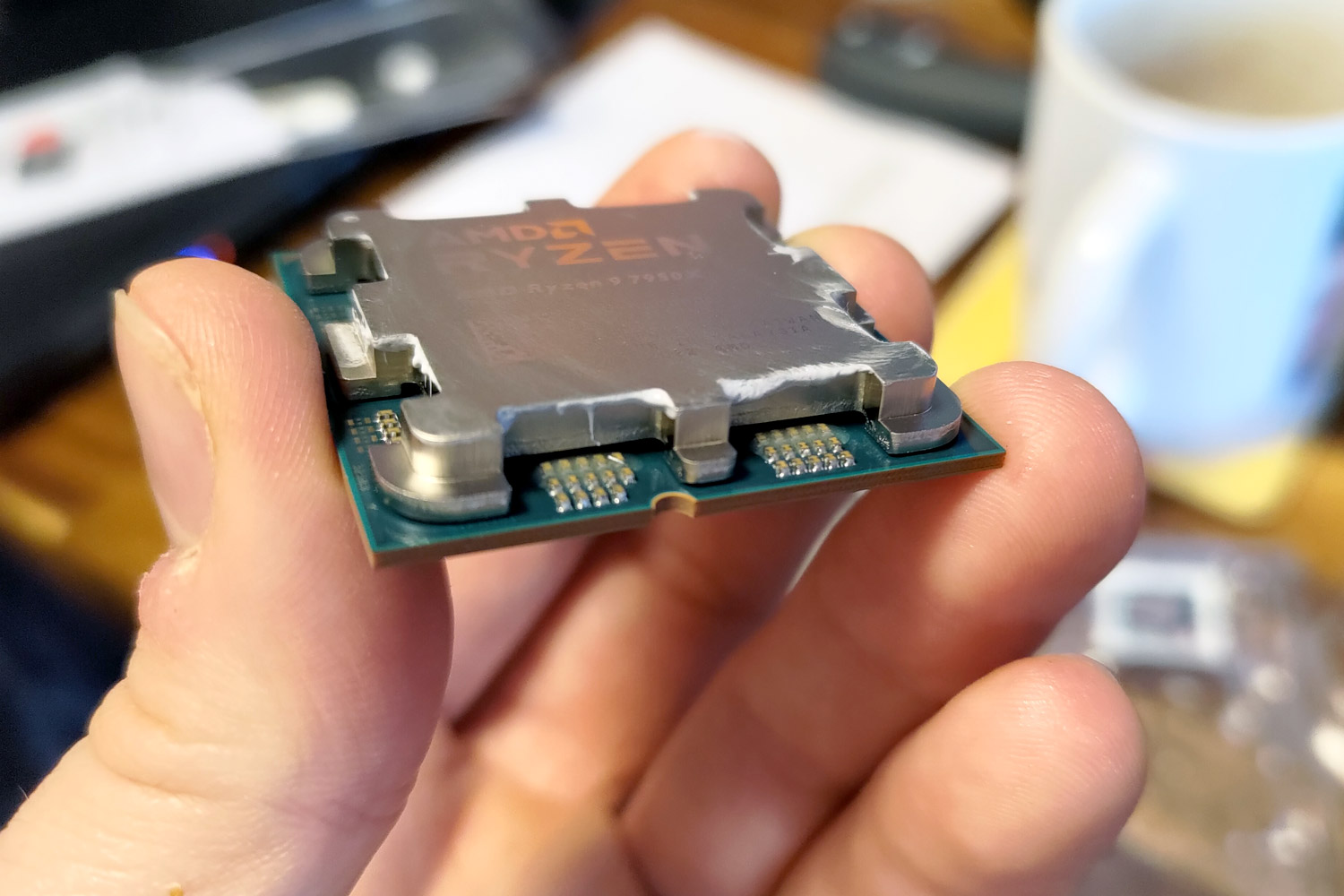
The term CPU stands for Central Processing Unit. It is the primary component of a computer that executes instructions from programs, enabling your device to function effectively. Originating in the early days of computing, the term reflects the central role the CPU plays in coordinating the operations of various hardware components.
Components of a CPU
Understanding the components of a CPU helps unravel its functionality:
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): The ALUCapability executes all arithmetic procedures and logical computational steps that include addition and subtraction together with comparison operations.
- Control Unit (CU): Through its design the CPU functions to transfer data between CPU memory and peripherals.
- Registers: Temporary storage units within the CPU that hold data and instructions for quick access.
The combination of these various components delivers efficient and seamless execution results.
How a CPU Works
The CPU operates through a systematic process known as the Fetch-Decode-Execute Cycle:
- Fetch: Their CPU retrieves an instruction that exists within the computer’s memory.
- Decode: The control unit serves the task of interpreting all received instructions.
- Execute: A set sequence of steps executes the instruction through number crunching functions and data transfers and logical assessments.
The latest generation of CPUs achieves efficient execution speeds through its parallel processing frameworks and pipelining capabilities.
Read More : Does a Better CPU Increase FPS _ The Ultimate Guide 2025
Types of CPUs
x86/x64 CPUs
These are designed for desktop computers, laptops, and servers:
- Intel: Numbered i3 i5 and i7 makeup Intel CPUs which excel at running different programs efficiently.
- AMD: With their Ryzen series gaining fame AMD presents users with strong processor alternatives that handle multitasking efficiently.
ARM CPUs
These are optimized for mobile devices, IoT, and low-power systems:
- CPUs exist in smartphones and tablets as well as embedded systems.
- The main emphasis in these designs centered around maximizing energy efficiency and maintaining optimal performance within small device form factors.
CPU Features That Matter Most

Clock Speed
The value of GHz (Gigahertz) measures how fast instructions proceed through a CPU. The relationship between performance speeds and the CPU’s clock speed remains direct.
Cores and Threads
Modern CPUs feature multiple cores, each capable of processing instructions independently:
- Current CPUs contain three main core configurations including Dual-Core and Quad-Core and Octa-Core.
- Additional processes run more efficiently through threads which enhance CPU performance during multitasking applications.
Cache Memory
Cache memory on CPUs appears in multiple levels such as L1, L2 and L3 which helps store common data operation requests to cut down processing time while enhancing CPU speed.
Power Efficiency
Performance optimization must consider energy usage because portable devices strongly depend on this measure.
Factors Affecting CPU Performance
Processor Architecture
CPU architecture generations including Intel’s Alder Lake and AMD’s Zen deliver better power management together with performance speed-ups which enhances dual-task abilities.
Thermal Management
Heat sinks and liquid cooling systems together act as dynamic cooling mechanisms for CPUs since these maintain proper performance levels while protecting against temperature stresses.
Overclocking
By upping the CPU’s base frequency speed users can engage in overclocking. Overclocking creates performance improvements yet the system needs effective cooling devices to stop equipment deterioration.
CPU vs. Other Components
The CPU interacts with key components like:
- RAM: The processor engages active data from the same storage area.
- GPU: Handles graphics-intensive tasks.
- Storage (HDD/SSD): Provides data for processing.
- Motherboard: A motherboard’s essential functionality enables it to link the CPU to different hardware devices.
Dynamic system equilibriums produce peak operational efficiency.
Read More : Cpu Temperature Monitor – The Complete Guide Of 2025!
Popular CPU Brands and Models
Intel CPUs
- Intel Core i9-13900K: This CPU delivers leading performance while maintaining gaming excellence together with enhanced productivity capacity.
- Intel Core i5-13600K: Mid-range powerhouse with balanced features.
AMD CPUs
- Ryzen 9 7950X: A top-tier CPU for creators and professionals.
- Ryzen 5 7600X: People who operate on limited budgets will appreciate this CPU because it delivers reliable performance.
ARM-Based CPUs
- Apple M1/M2: The M1/M2 processor from Apple brings unprecedented efficiency and power to Apple devices.
Choosing the Right CPU
For Gaming
- When searching for a CPU you should select models which operate at high speeds and have multiple core capability.
- Examples: Intel Core i7-13700K, AMD Ryzen 7 7800X.
For Productivity
- The CPU selection should focus on multiple cores alongside plenty of threads.
- Examples: Ryzen 9 7950X, Intel Core i9-13900K.
For Everyday Use
- Budget-friendly CPUs with sufficient power.
- Examples: Intel Core i3-13100, AMD Ryzen 5 5600X.
Tips to Optimize CPU Performance
- Keep Software Updated: It is essential to keep your operating system together with your device drivers at their most recent versions.
- Manage Background Processes: Limit unnecessary programs running simultaneously.
- Ensure Adequate Cooling: Invest in quality cooling solutions.
- Upgrade Hardware: Adding an SSD together with additional RAM creates a performance boost for your CPU.
The Future of CPUs
Innovations in CPU technology include:
- AI-Driven CPUs: Machine-learning alongside artificial intelligence comprises this system’s optimized functions.
- Quantum Computing: Promising unprecedented processing power.
- Neuromorphic Chips: A unique technology built to emulate actual human brain processing characteristics.
FAQs
1. In computers what does the acronym CPU represent?
In computing a CPU functions as the Central Processing Unit to perform program instructions while running computer operations.
2. What makes the CPU earn its title as the computer’s brain?
Just as brains process information, the CPU delivers this function through its interpretation and execution of commands.
3. When comparing computers, how do the CPU and the GPU compare?
Uniquely the CPU manages complete system instructions yet it shares processor space with the GPU which excels at graphics production and parallel operation management.
4. What indicators tell me if my CPU has enough speed?
A CPU evaluation must include its frequency speed alongside core quantity as well as system requirements testing.
5. How can I upgrade my CPU?
Before upgrading you must check your motherboard’s compatibility and assess the need for a cooling system.

