To identify your CPU cooler, check for labels on the cooler, use system-monitoring software, or refer to documentation, the manufacturer’s website, or online forums for assistance.
How To See What Cpu Cooler I Have Overview:

If you’re looking to upgrade your system or troubleshoot performance issues, knowing which CPU cooler you have installed is essential. Your cooler plays a vital role in maintaining optimal temperatures for your CPU, especially during demanding tasks like gaming, video rendering, or heavy multitasking. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to identify your CPU cooler easily and effectively.
Check the Physical Cooler:
The most straightforward way to see what CPU cooler you have is to physically inspect it. Here’s how to do it safely:
Step-by-Step Guide:
- Power Down Your PC: Before you start, make sure to shut down your computer completely and unplug it from the power source to prevent any electrical hazards. Wait a few minutes to ensure all components have cooled down.
- Open the Case: Use a screwdriver to remove the side panel of your computer case. Be cautious not to touch any components unnecessarily to avoid static electricity damage.
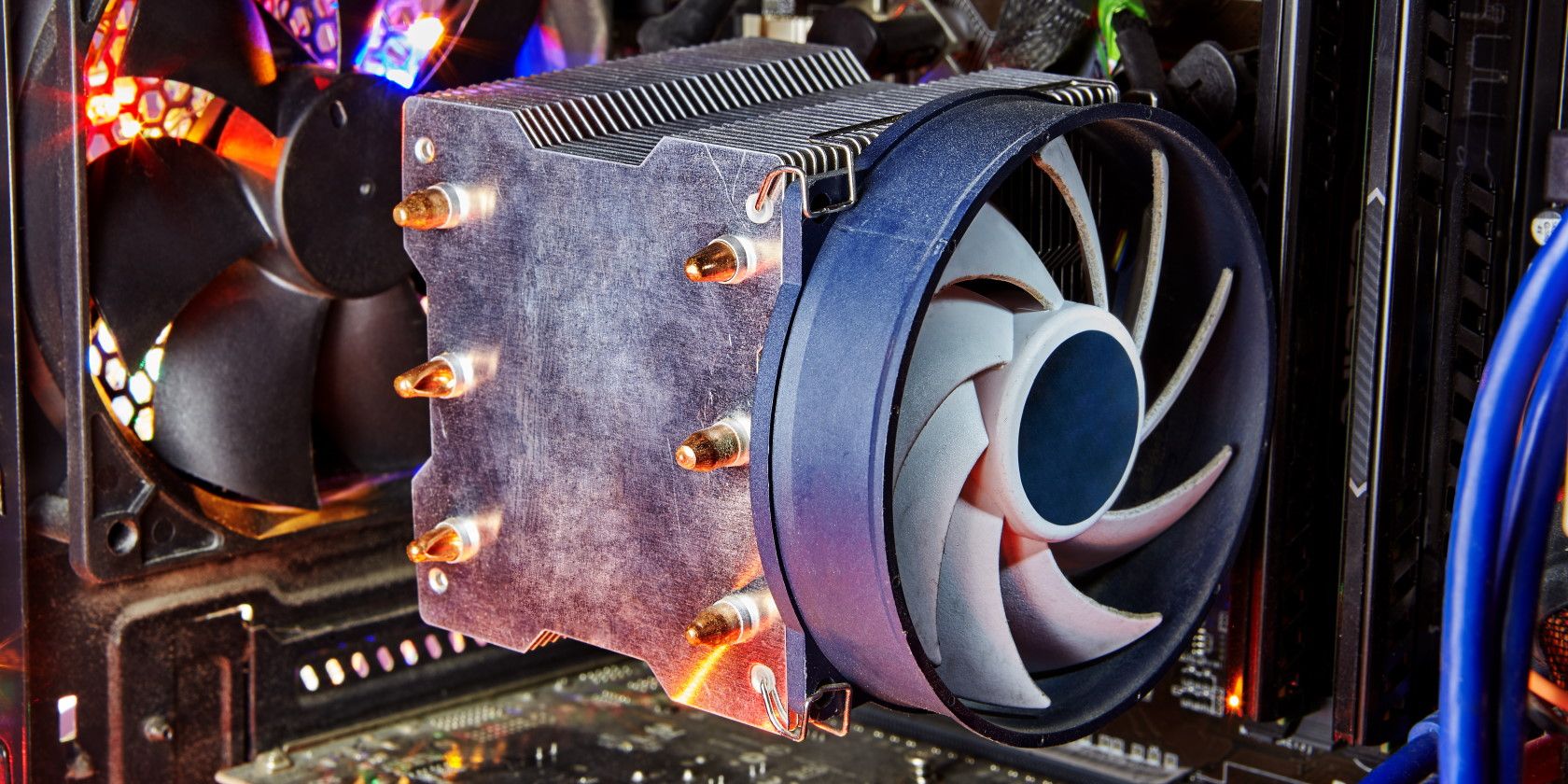
- Locate the CPU Cooler: Look for the cooler on top of the CPU socket. Most coolers are either air-based with large heatsinks and fans or liquid cooling systems with radiators and tubes.
- Check for Labels: Many coolers have stickers or labels on them that indicate the brand and model. Take note of this information for future reference. If the cooler is not easily visible, you may need to remove any fans or shrouds that are obstructing your view.
- Take Photos: If you’re unsure about the cooler model, taking clear photos can help you later when researching or asking for advice in forums.
How Do I Match My CPU Cooler?
To match your CPU cooler, start by checking the CPU socket type and size compatibility. Each CPU model fits specific sockets (such as LGA1200 or AM4), so the cooler must match your processor’s socket type. Consider your CPU’s thermal design power (TDP) as well—higher TDPs require more powerful cooling solutions to handle heat effectively. Measure your PC case’s clearance to ensure the cooler will fit, and choose between air coolers and liquid coolers based on your cooling needs and available space.
Read More: Can I Use 70 Isopropyl Alcohol To Clean Cpu – A Guide Of 2024!
Use Software Tools:
If you prefer not to open your computer, you can use software tools to identify your CPU cooler. While these tools may not provide the exact model, they can give you useful information about your cooling solution.
Recommended Software:
Several software tools can assist you in gathering detailed information about your CPU cooler and overall system performance. CPU-Z is a popular application that provides comprehensive information about your CPU and motherboard. Although it may not directly display your cooler model, it helps you identify your CPU, enabling you to research compatible cooling solutions.
HWMonitor is another valuable tool that provides temperature readings, helping you evaluate the effectiveness of your current cooling solution by showing the temperatures of various components, including your CPU, and displaying fan speeds, which can indicate how well your cooler is functioning.
Speccy is a comprehensive system information tool that offers insights into your CPU, motherboard, and other hardware components, giving you a clearer picture of your system setup, although it may not specifically name your cooler. Lastly, Open Hardware Monitor delivers real-time data on CPU temperatures, fan speeds, and load percentages, providing insights into your cooler’s effectiveness, even if it doesn’t specify the cooler model itself.
Check Your Documentation:
If you still have the original packaging or documentation for your CPU cooler, this can be an excellent resource. Look for the installation guide or product specification sheet that came with your cooler. This information can help you identify the cooler model and its features. If you don’t have the physical documentation, you can often find manuals and specifications online by searching for the cooler brand and model number.
Visit the Manufacturer’s Website:
If you remember the brand of your cooler but not the specific model, visit the manufacturer’s website. Most brands have a product catalog that allows you to browse through their offerings. You can often find detailed specifications, images, and installation guides to help identify your cooler. This is also a good opportunity to check for firmware updates or compatibility information if you’re considering an upgrade.
Seek Help from Online Communities:
Online forums and communities can be invaluable resources for identifying computer components. Websites like Reddit, Tom’s Hardware, or even specialized PC-building forums can assist. You can post a picture of your cooler or describe it, and other users can help you identify it. When seeking help, be sure to provide as much detail as possible, including your CPU model and any other relevant information about your setup.
Consider Upgrading Your CPU Cooler:
Once you’ve identified your CPU cooler, consider whether it meets your performance needs. If you’re experiencing overheating issues or if you plan to overclock your CPU, upgrading to a more efficient cooler may be a wise choice.
Read More: Why Does My Cpu Fan Start And Stop – A Complete Guide Of
Types of Coolers to Consider:
- Air Coolers: These are the most common type and come in various sizes. High-end air coolers often provide excellent cooling performance at a lower price point than liquid coolers.
- Liquid Coolers: Liquid cooling systems typically offer superior cooling performance and quieter operation, making them ideal for high-performance CPUs. They can be more expensive and may require more maintenance, but they often provide better thermal performance, especially for overclocking.
- All-in-One (AIO) Coolers: These liquid coolers come pre-assembled and are easier to install than custom liquid cooling systems. They provide good performance and aesthetics without the complexity of custom setups.
How Do I Check My CPU Cooler Temperature?
To check your CPU cooler’s temperature, use system monitoring software like Core Temp, HWMonitor, or your motherboard’s software. These tools allow you to monitor real-time CPU temperature readings. In Windows, you can also access basic temperature information in the BIOS settings by restarting your computer and entering the BIOS menu. Ideally, your CPU should remain between 40-70°C under normal loads, and stay below 85°C during intensive tasks.
Maintenance Tips:
Regular Dusting:
Keep your cooler free of dust and debris. Dust can accumulate over time, reducing airflow and cooling efficiency. Use compressed air to blow out dust from the heatsink and fans. Regularly inspecting your cooler for dust buildup, especially in environments with high dust levels, can prevent overheating and prolong the life of your components. Additionally, consider implementing dust filters in your PC case to minimize future dust accumulation and maintain optimal airflow.
Reapply Thermal Paste:
Over time, the thermal paste can dry out, leading to less effective heat transfer. Consider reapplying thermal paste every few years or after replacing your cooler. When reapplying, ensure that both the CPU and cooler surfaces are thoroughly cleaned to remove the old thermal paste, as any residue can hinder performance. Additionally, use a high-quality thermal paste and apply it in a thin, even layer to ensure optimal thermal conductivity and cooling efficiency.
Monitor Temperatures:
Keep an eye on your CPU temperatures, especially during demanding tasks. If you notice spikes, it might be time to check your cooler’s functionality or consider an upgrade. Utilize software tools like HWMonitor or Core Temp to track real-time temperatures and ensure they remain within safe operating limits. Regular monitoring can help you proactively address cooling issues before they lead to overheating or potential hardware damage.
FAQs:
1. How can I find out what CPU cooler I have?
Inspect your cooler for labels or branding, use software like HWMonitor, or refer to documentation and the manufacturer’s website.
2. What tools can I use to monitor my CPU cooler’s temperature?
Tools like Core Temp, HWMonitor, and BIOS settings display real-time temperature readings for your CPU and cooling system.
3. Why is it important to know my CPU cooler type?
Knowing your cooler type helps in troubleshooting and choosing compatible upgrades for optimal CPU cooling performance.
4. What’s the difference between air and liquid CPU coolers?
Air coolers are cost-effective and efficient, while liquid coolers provide superior cooling, particularly for overclocking, albeit at a higher cost.
5. How often should I clean my CPU cooler?
Clean your CPU cooler regularly to prevent dust buildup that reduces cooling efficiency, ideally every few months, depending on environmental conditions.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, identifying your CPU cooler is crucial for maintaining optimal system performance and addressing overheating issues. By physically inspecting the cooler, utilizing software tools, or consulting manufacturer resources, you can easily determine the model you have. Furthermore, understanding your cooler’s specifications will help you make informed decisions about upgrades, ensuring your CPU operates efficiently under demanding workloads.


I’d like to find out more? I’d love to find out more details.