OC is Not Supported CPU means that your processor does not allow overclocking, limiting its performance to the manufacturer’s specified range. For CPUs that support overclocking, look for “K” or “X” models, and ensure compatibility with your motherboard and cooling system.
OC Is Not Supported CPU
When building a high-performance PC or tuning your current system for better performance, overclocking (OC) is a frequently discussed topic. Overclocking allows you to push your CPU beyond its stock performance limits.
However, not all processors support this feature. If you’ve come across the message “OC is not supported CPU,” you may be wondering what it means and how it impacts your options. In this guide, we’ll explore why some CPUs do not support overclocking, how to check if your processor is one of them, and the alternatives you can pursue to enhance your system’s performance.
What Does OC Is Not Supported CPU Mean?
The phrase “OC is not supported CPU” indicates that your processor does not support overclocking. Overclocking refers to adjusting a processor’s clock speed to make it run faster than its standard specification, which can improve system performance, particularly in tasks like gaming, video editing, and rendering.
However, CPUs are either locked or unlocked based on their design. A locked CPU has predefined performance limits set by the manufacturer, and attempting to exceed those limits can lead to instability or even damage.
In simple terms, a locked CPU cannot increase its core frequency beyond the manufacturer’s designated range, hence “OC is not supported.”
How to get a supported CPU?
To ensure you get a supported CPU, start by verifying your motherboard’s compatibility using its official website for a CPU support list. For older motherboards, a BIOS update may be necessary to accommodate newer CPUs, so check for the latest version from the manufacturer.
Confirm the chipset’s compatibility with the CPU generation you’re considering, like how Intel 12th Gen CPUs often require 500-series motherboards. Buy from reputable retailers to avoid counterfeit products, and consider future-proofing by selecting newer CPUs that offer ongoing support for future software and games. These steps will help with troubleshooting CPU issues and optimizing your system’s performance.
Why Some CPUs Don’t Support Overclocking?
CPU Model Designation:
Both Intel and AMD manufacture two types of processors: locked and unlocked. Unlocked CPUs allow for overclocking, while locked CPUs do not.
Read More: Can Cpu Run Without Thermal Paste – A Complete Guide Of 2024!
Intel Processors: Intel’s unlocked processors are designated with a “K” or “KF” suffix in the model name (e.g., Intel Core i7-9700K). Non-K models (e.g., Intel i5-9400) are locked and overclocking is not supported.
- AMD Processors: AMD Ryzen CPUs with an “X” in their model name (e.g., Ryzen 7 3700X) offer overclocking capabilities, while some non-X models are locked or offer limited overclocking support.
Locked CPUs are designed to offer stable performance under stock settings, which can be advantageous for users who prioritize reliability and longevity over maximizing performance.
Maintaining Stability and Longevity:
Overclocking a CPU generates extra heat and demands more power, which can reduce the overall lifespan of the hardware if not properly managed. Manufacturers lock CPUs to prevent users from unintentionally damaging the processor through overclocking. Locked CPUs are more suitable for everyday users and professionals who require reliable performance without the risks associated with overclocking.
Target Audience and Use Case:
Processors that do not support overclocking are often marketed toward general consumers who need a dependable computing experience. These users may be performing tasks like web browsing, media consumption, office work, and casual gaming—tasks that don’t require the extreme performance boosts overclocking can provide. For such purposes, locked CPUs offer excellent out-of-the-box functionality without the need for advanced cooling systems or high-performance power supplies.
What Happens if CPU is Not Supported?
If your CPU is not supported by the motherboard or system, several issues may occur:
- System Won’t Boot: The computer may fail to boot, showing either a black screen or a BIOS error message. Incompatible CPUs are often not recognized by the motherboard, leading to a non-functional system.
- Crashes and Instability: Even if the system boots, the CPU may cause frequent crashes, blue screens, or instability in programs and processes due to mismatched hardware compatibility.
- Limited Functionality: Unsupported CPUs may not allow certain features such as multi-core processing, hyper-threading, or power-saving functionalities, resulting in poor performance.
- BIOS Error Messages: You’ll likely receive error messages from the BIOS, often indicating an unsupported or unrecognized CPU model.
How to Check If Your CPU Supports Overclocking?

Not sure if your CPU supports overclocking? Here’s how you can check:
Model Name Check:
As previously mentioned, the easiest way to determine if your CPU supports overclocking is to check the model name:
- Intel: Look for the “K” suffix (e.g., i7-10700K). If there’s no “K” (e.g., i5-10400), your CPU is locked.
- AMD: Check for the “X” designation in Ryzen processors (e.g., Ryzen 5 5600X). Non-X models may have limited overclocking support, but they generally won’t offer the same flexibility.
Consult the Manufacturer’s Specifications:
You can visit Intel or AMD’s official websites to review the specifications of your processor. This will tell you whether the CPU is designed for overclocking or if it has a locked multiplier.
Check Your BIOS Settings:
Enter your BIOS settings (usually by pressing a key like **Delete** or **F2** during startup) and look for overclocking-related options. If these options are unavailable or greyed out, your CPU is likely locked.
Why Is My CPU Overclock Not Working?
Several factors can prevent successful CPU overclocking:
- Locked Processor: Some CPUs, especially those not designed for overclocking (non-K series for Intel or non-X series for AMD), have locked multipliers, making overclocking impossible.
- BIOS Limitations: Your motherboard’s BIOS may not support overclocking features or may have restrictions on certain CPUs.
- Insufficient Cooling: Overclocking generates more heat, and without adequate cooling solutions, the CPU may throttle or shut down to prevent overheating.
- Power Supply Limitations: Overclocking increases power consumption, and a weak or insufficient power supply may limit your ability to overclock effectively.
- Unstable Settings: Incorrect voltage or frequency settings can lead to instability, crashes, or system failures.
Read More: Can You Flash BIOS with CPU Installed – A Complete Guide Of
What Are the Alternatives to Overclocking?
If you own a CPU that doesn’t support overclocking, there are still several ways to optimize performance without pushing the processor beyond its standard limits:
Optimize Cooling and Power Supply:
To optimize cooling and power supply in a system where overclocking isn’t an option, maintaining low CPU temperatures is crucial in preventing thermal throttling, where the processor slows down to avoid overheating.
There are several steps you can take to improve cooling and ensure stable power delivery. First, consider installing a better cooling solution, such as upgrading to a high-performance air cooler or liquid cooling system to keep CPU temperatures lower.
Additionally, ensuring adequate airflow in your case by adding more fans or improving cable management can significantly enhance cooling efficiency. Lastly, upgrading your power supply to a high-quality PSU ensures stable power delivery, improving both the longevity and overall stability of your CPU.
Memory Overclocking:
Even if your CPU is locked, you may still be able to overclock your RAM. By enabling XMP (Intel) or DOCP (AMD) in your BIOS, you can push your memory modules beyond their default speeds, which can result in better overall system performance, especially in tasks that require high memory bandwidth.
Optimize Software Settings:
To improve system performance, it’s essential to update all your hardware drivers, particularly the CPU, GPU, and chipset, as this can enhance compatibility and overall efficiency.
Additionally, closing unnecessary background processes helps free up valuable CPU resources, allowing more power for intensive tasks. Adjusting your power settings on Windows or macOS by switching to “High Performance” mode also ensures that maximum resources are allocated to the CPU and other critical hardware, further optimizing performance.
Consider a CPU Upgrade:
If overclocking is crucial for your workflow or gaming experience, consider upgrading to an unlocked processor. Intel’s K-series CPUs or AMD’s X-series CPUs will allow you to push your system’s performance much further than a locked processor can. Keep in mind, however, that overclocking requires a more powerful cooling system and potentially a stronger PSU.
How Do I Enable Overclocking on My CPU?
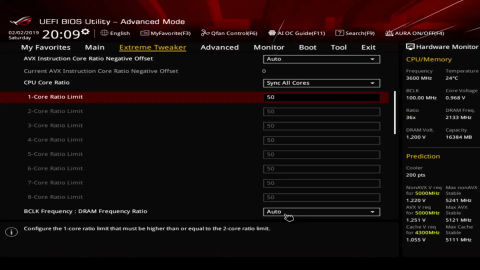
To enable CPU overclocking, follow these general steps:
- Check CPU and Motherboard Compatibility: Ensure your CPU is unlocked (e.g., Intel K-series or AMD Ryzen) and the motherboard supports overclocking (e.g., Z-series chipset for Intel, X or B series for AMD).
- Update BIOS: Make sure your motherboard has the latest BIOS version, as updates may include better overclocking support.
- Enter BIOS/UEFI Settings: Restart your PC and enter the BIOS/UEFI menu by pressing the appropriate key (e.g., F2, DEL, or ESC) during startup.
- Adjust CPU Clock Multiplier: In the overclocking section of BIOS, increase the CPU multiplier (ratio) to raise the CPU clock speed.
- Increase Voltage (Optional): If the system becomes unstable, slightly increasing the CPU voltage (Vcore) may help stabilize the overclock.
- Test Stability: Use stress-testing software (e.g., Prime95, AIDA64) to test your system’s stability and monitor temperatures to avoid overheating.
- Save Settings: Once satisfied, save the changes in BIOS and reboot your system.
The Benefits and Drawbacks of Overclocking:
Before deciding whether to upgrade to an overclockable CPU, consider the pros and cons of overclocking:
Pros of Overclocking:
Overclocking can be an enticing option for enthusiasts looking to squeeze extra performance from their system without investing in new hardware. The performance boost from overclocking is particularly noticeable in CPU-heavy tasks such as gaming, 3D rendering, video editing, and encoding.
Gamers benefit from higher frame rates, while content creators experience faster rendering times, making overclocking a valuable tool for demanding workloads. Additionally, it’s a cost-effective solution, allowing users to prolong the lifespan of their system by extracting more power from their current components, rather than upgrading to newer, more expensive hardware.
Cons of Overclocking:
Cons of overclocking include increased heat and power consumption, putting more strain on components like the motherboard and PSU. A high-quality cooler and sometimes an upgraded PSU is necessary to maintain stability. Overclocking risks system instability, with potential crashes or hardware damage if not carefully managed.
It can also void warranties, leaving users unprotected if damage occurs. Achieving a stable overclock requires advanced knowledge, fine-tuning of settings, and careful monitoring of performance and temperatures. Lastly, it demands patience and experience to balance voltage and clock speeds effectively.
FAQs:
1. What does “OC is Not Supported CPU” mean?
It means your processor does not support overclocking, preventing any adjustments to the CPU’s clock speed beyond the factory settings.
2. Why don’t some CPUs support overclocking?
Some CPUs are locked by the manufacturer to maintain stability and prevent hardware damage from overclocking.
3. How can I tell if my CPU supports overclocking?
Check if your CPU has a “K” (Intel) or “X” (AMD) in its model name, or consult the manufacturer’s website.
4. What are alternatives to overclocking a locked CPU?
You can optimize your system’s performance through better cooling, memory overclocking, or upgrading to a supported CPU.
5. What happens if you use an unsupported CPU?
If your CPU is unsupported, the system may fail to boot, experience crashes, or show error messages in BIOS.
Conclusion:
If your CPU does not support overclocking, its performance remains limited to the manufacturer’s predefined range. To overclock, choose unlocked CPUs with designations like Intel’s “K” or AMD’s “X” series and ensure motherboard compatibility. While overclocking can boost performance, alternatives like improving cooling, optimizing software, or upgrading hardware are viable for locked CPUs.

